E-WISH: An Energy-aware ABR Algorithm For Green HTTP Adaptive Video Streaming
ACM Mile-High Video 2024
Marriott DTC, Denver, Feb. 11 – 14, 2024
[PDF]
Daniele Lorenzi (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt, Austria), Minh Nguyen (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt, Austria), Farzad Tashtarian (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt, Austria), and Christian Timmerer (Alpen-Adria-Universität Klagenfurt, Austria)
Abstract:
HTTP Adaptive Streaming (HAS) is the prevailing solution for transmitting video content over the Internet. The urgency of the climate crisis has brought attention to the environmental impact of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) solutions, emphasizing the necessity for eco-friendly alternatives to mitigate ICT’s carbon footprint. In the context of HAS, Adaptive Bitrate (ABR) algorithms are commonly employed to determine which video segments to retrieve. However, these algorithms typically prioritize video quality without considering the energy implications of their decisions. Consequently, they often opt for the highest bitrate video representation in favorable network conditions, leading to increased energy consumption.
To tackle these issues, we introduce E-WISH, a novel energy-aware ABR algorithm. E-WISH builds upon
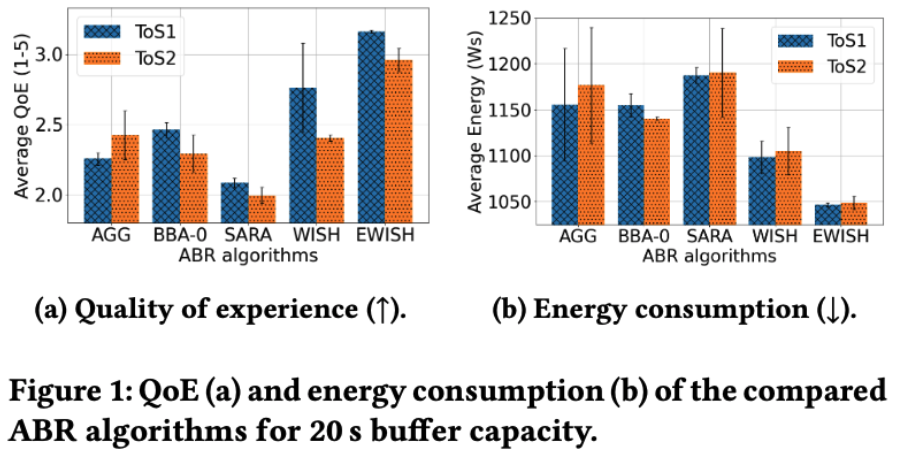
the existing WISH algorithm by extending its capabilities to account for energy consumption when selecting the quality for the next video segment. Implemented on the client side, E-WISH considers the available throughput, player buffer, video quality, and energy consumption as costs in determining the optimal representation for the upcoming video segment. Experimental results demonstrate that E-WISH can enhance the Quality of Experience (QoE) by up to 52%, as per the ITU-T P.1203 model (mode 0), compared to existing state-of-the-art approaches while reducing the energy consumption on the device by up to 12%, as measured using the Voltcraft © VC-7200BT3 digital multimeter.