Video streaming in numbers
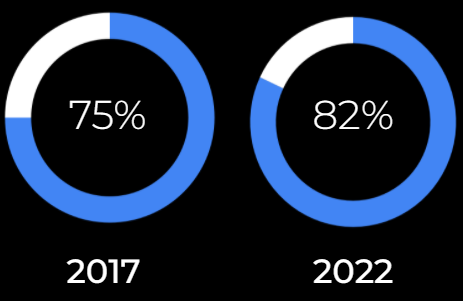
Video streaming has been growing so fast in global Internet traffic. Its data occupancy in 2017 counted for 77% of global Internet traffic. Cisco estimated that it will reach 82% by the end of 2022. However, viewers still experience video streaming issues like video lagging a.k.a rebuffering or low quality video… Now, HTTP Adaptive Streaming is a solution for that.
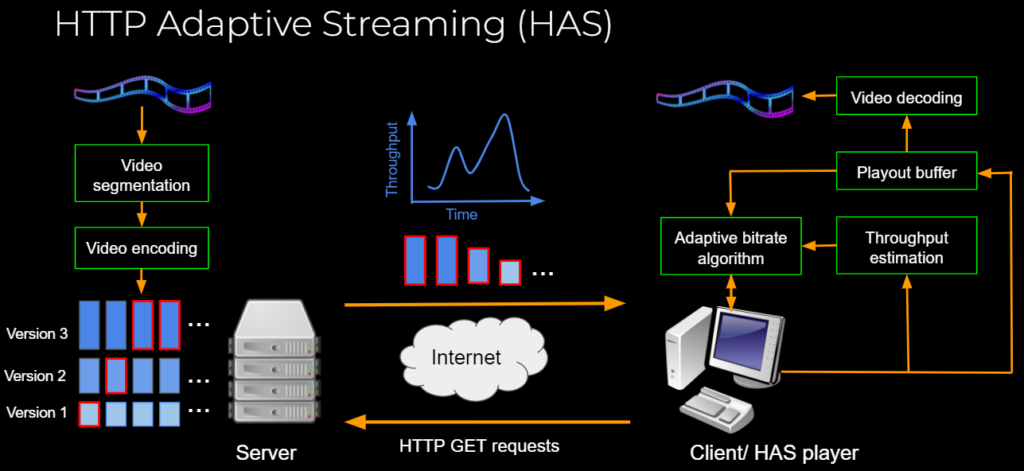
Overview of HTTP Adaptive Streaming
HTTP Adaptive Streaming has become a predominant technique for delivering video over the Internet. In HTTP Adaptive Streaming, multiple versions are generated from an original video at the server in order to adapt to the network. Each version is then divided into temporal segments of the same duration. The client sends HTTP requests for the most suitable versions for the video segments based on an adaptive bitrate (ABR) algorithm. The ABR algorithm can rely on the client parameters such as buffer status, or network parameters such as throughput.
So, why do we need to encode videos at different versions? There are 2 reasons.
First, the throughput, especially from mobile networks, fluctuates a lot. This requires the client to decrease to a lower version with smaller bitrate to avoid rebuffering. Or the client needs to jump to a higher version for a better quality. For example, when the network is only 1Mbps,the client might download 700kbps only with 480p resolution. However, if the network is better, let say 20Mbps, we should download a 4K video with 12Mbps for much better quality.
Second, the viewers are using heterogeneous devices to watch that video over HTTP such as mobiles, tablet, desktop, and TV. A mobile doesn’t need a 4K video as the screen is too small but a TV does.
Challenges
What are the challenges of HTTP Adaptive Streaming? Well, both industry and academy are focusing on some popular challenges as follows:
- Live latency
- Throughput prediction
- Quality of Experience (QoE)
- Rebuffering and video quality
And these problems are waiting for you to solve.
If you are interested in what we are working on, please take a look here.
0 thoughts on “What you should know about HTTP Adaptive Streaming?”